Kth Smallest Instructions
Problem
Bob is standing at cell , and he wants to reach destination: . He can only travel right and down. You are going to help Bob by providing instructions for him to reach destination.
The instructions are represented as a string, where each character is either:
- , meaning move horizontally (go right), or
- , meaning move vertically (go down). Multiple instructions will lead Bob to destination. For example, if destination is , both and are valid instructions.
However, Bob is very picky. Bob has a lucky number , and he wants the lexicographically smallest instructions that will lead him to destination. is 1-indexed.
Given an integer array and an integer , return the lexicographically smallest instructions that will take Bob to destination.
Example
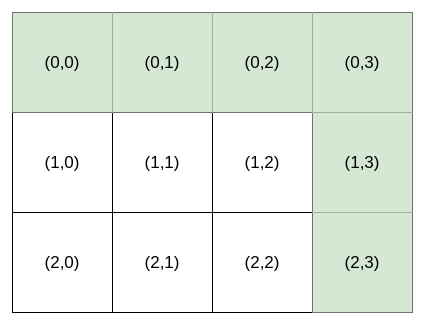
Input: destination = [2,3], k = 1
Output: "HHHVV"
Explanation: All the instructions that reach (2, 3) in lexicographic order are as follows:
["HHHVV", "HHVHV", "HHVVH", "HVHHV", "HVHVH", "HVVHH", "VHHHV", "VHHVH", "VHVHH", "VVHHH"].
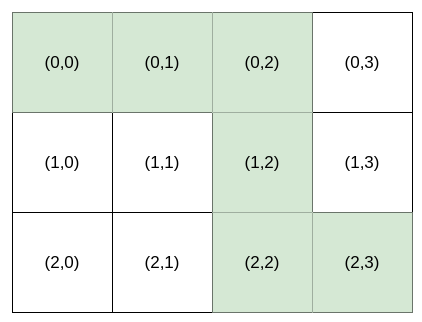
Input: destination = [2,3], k = 3
Output: "HHVVH"
Constraints
- , where denotes a choose b
Submit your solution at here
Solution
Intuition
I solve this in 2 steps:
- Count possible ways to reach all
- Travel from , in each step, greedily decide if we should go right or down
- If we go right, our rank stay the same, since is the best choice lexicography
- If we go left, our rank decrease, we choose which essentially go down lexicography. Use precalculated array from previous step to determine how many rank do we go down
- When we reach , answer is the path made from the traversal
Code
class Solution {
public:
string kthSmallestPath(vector<int>& destination, int k) {
int n = destination[1]+1;
int m = destination[0]+1;
vector<vector<int>> f(n, vector<int>(m,0));
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {
f[i][0] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) {
f[0][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1;i<n;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j<m;j++) {
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j] + f[i][j-1];
}
}
string ret = "";
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int rank = 1;
while(i<n && j<m) {
int dx = n-1-i;
int dy = m-1-j;
if(dx == 0 && dy == 0) {
break;
}
if(dx == 0) {
j++;
ret += "V";
} else if(dy == 0) {
i++;
ret += "H";
} else {
int deltaV = f[dx][dy] - f[dx][dy-1];
// if we go down, we go down deltaV in rank
// if we go right, our rank stay the same
if(rank + deltaV <= k) {
rank += deltaV;
j++;
ret += "V";
} else {
i++;
ret += "H";
}
}
}
return ret;
cout<<"f: "<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j<m;j++) {
cout<<f[i][j]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
return ret;
}
};